Disseminated Staphylococcal Infection Induced Rapidly Progressive Gangrene of Skin in a Preterm Neonate-Purpura Fulminans
Sisodiya RS, Ratan KS
DOI10.21767/2573-0282.100020
Sisodiya RS* and Ratan KS
Department of Pediatric Surgery, MAMC and Associated Lok Nayak Hospital, New Delhi, India
- *Corresponding Author:
- Sisodiya RS
Department of Pediatric Surgery
MAMC and Associated Lok Nayak Hospital
New Delhi-110002, India
Email: sisodiyarajpalsingh@yahoo.in
Received date: July 05, 2016; Accepted date: July 06, 2016; Published date: July 07, 2016
Citation: Sisodiya RS and Ratan KS (2016) Disseminated Staphylococcal Infection Induced Rapidly Progressive Gangrene of Skin in a Preterm Neonate-Purpura Fulminans. Pediatric Infect Dis 1:20. doi: 10.21767/2573-0282.100020
Abstract
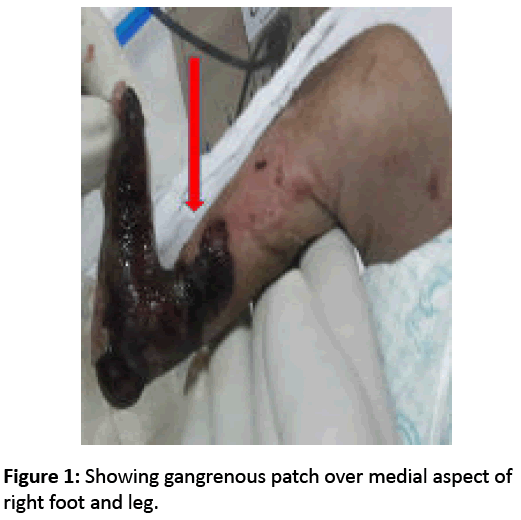
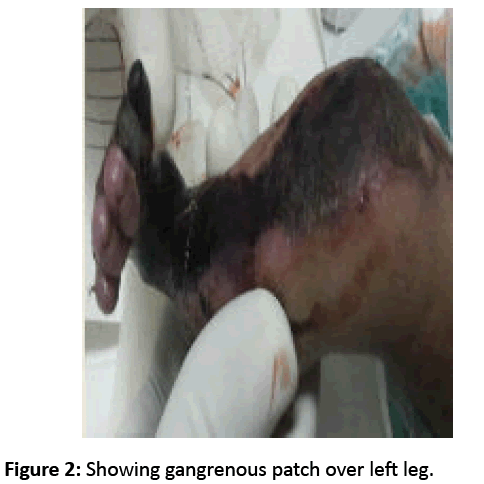
A preterm (34 weeks) 1.5 kg, 72 hours old male neonate presented with letharginess, vomiting, and black patches over body since 24 hours. On examination baby was in shock and there was disseminated gangrenous skin patches over bilateral upper and lower limb (Figures 1 and 2), back and abdomen. Child was intubated, resuscitated and kept on ventilation and inotropes. Investigation reveals haemoglobin 12.3 gm, Leucocytosis, thrombocytopenia, deranged kidney function test and coagulation profile. Culture from gangrenous skin and blood showed growth of Staphylococcus aureus. Appropriate supportive management was contemplated but child ultimately succumbed within 24 hours of admission.
Image Article
A preterm (34 weeks) 1.5 kg, 72 hours old male neonate presented with letharginess, vomiting, and black patches over body since 24 hours. On examination baby was in shock and there was disseminated gangrenous skin patches over bilateral upper and lower limb (Figures 1 and 2), back and abdomen. Child was intubated, resuscitated and kept on ventilation and inotropes. Investigation reveals haemoglobin 12.3 gm, Leucocytosis, thrombocytopenia, deranged kidney function test and coagulation profile. Culture from gangrenous skin and blood showed growth of Staphylococcus aureus. Appropriate supportive management was contemplated but child ultimately succumbed within 24 hours of admission.
Neonatal Purpura fulminans (PF) is a dermatological expression of haemorrhagic infarct due to intravascular thrombosis secondary to bacterial infections or deficiency of anticoagulants such as protein C and protein S. Neonatal PF is a rare disorder and associated with a high mortality [1,2]. Although group B streptococcus has been found as common cause of infectious PF, Staphylococcus aureus induced PF has been described [1,3,4].
References
- Elayappen A, Jain SK, Loeffelholz MJ, Patel J (2014)Purpurafulminans and late onset group B streptococcal sepsis in a premature twin. AJP Rep 4:e69-72.
- Albarrak M, Al-Matary A (2013) Neonatal purpurafulminans manifestation in early-onset group B Streptococcal infection. Am J Case Rep14:315-317.
- VermaP, Pandhi D, Yadav P, Dhawan AK (2013) Neonatal purpurafulminans due to methicillin resistant Staphylococcusaureus. PediatrDermatol 30:266-267.
- Hon KL, So KW, Wong W, Cheung KL (2009) Spot diagnosis: An ominous rash in a newborn. Ital J Pediatr 35:10.
Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences